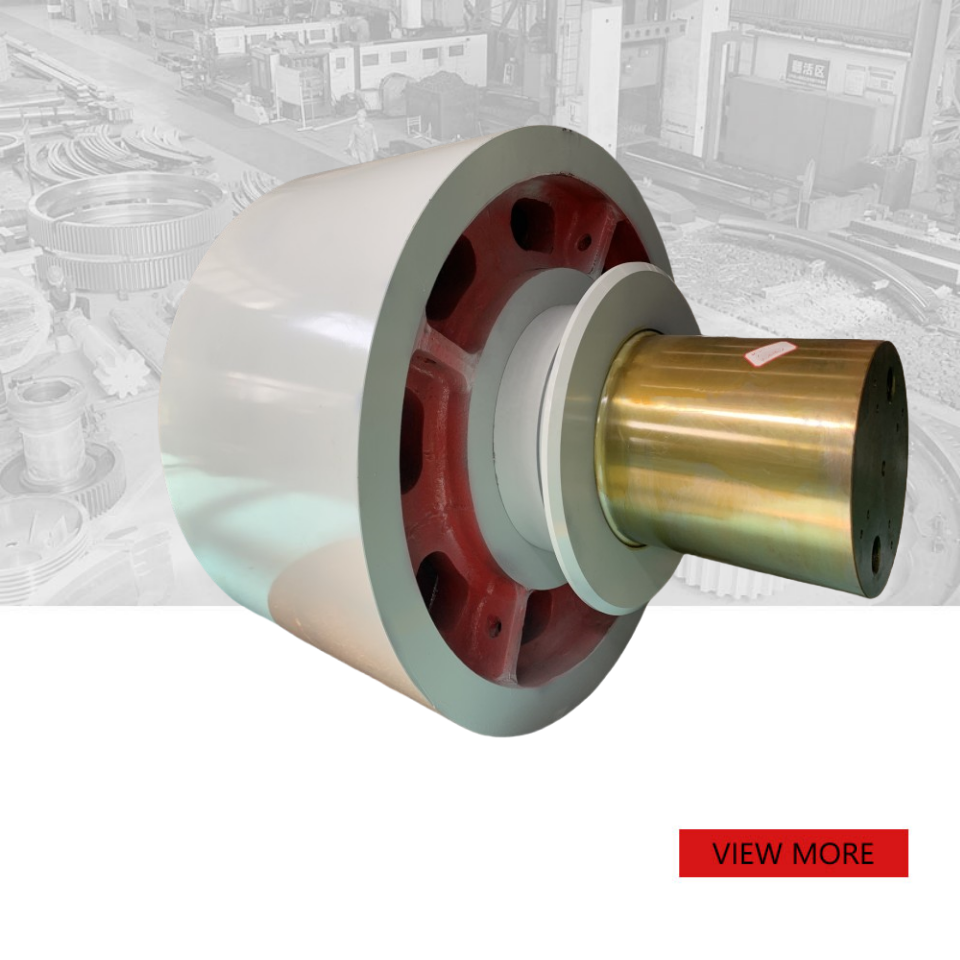
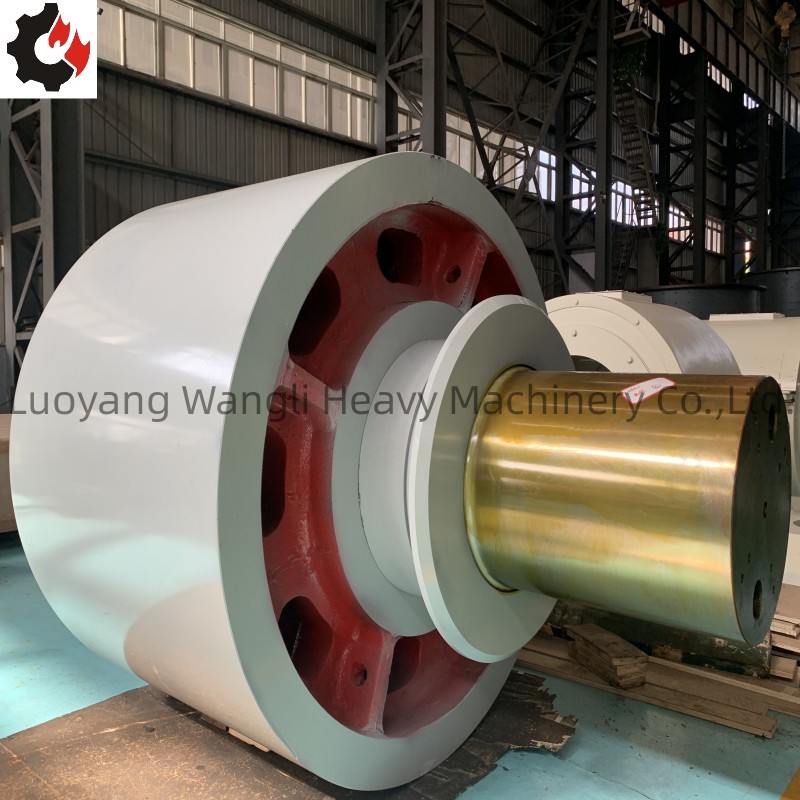
Custom casting large support roller
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Description
General processing flow of cast support roller:
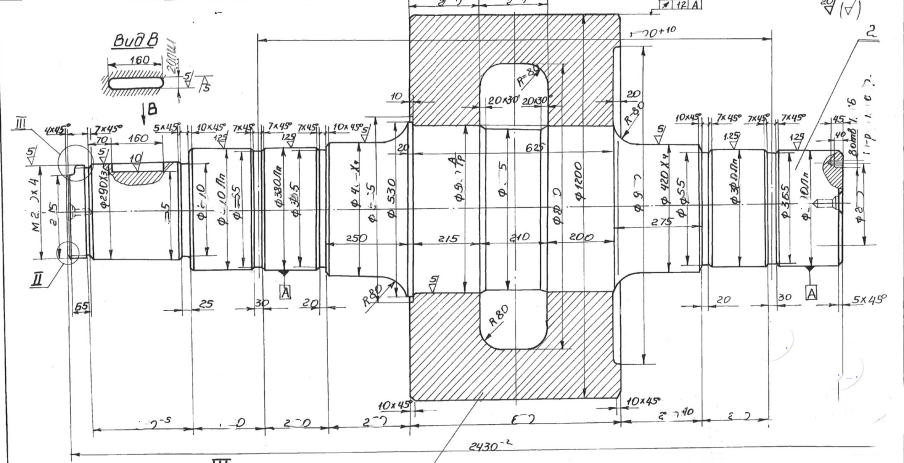
1: Design and engineering analysis:
According to the specific requirements and working conditions of the rotary kiln, engineers will design the size, shape and structure of the support roller.
Use computer-aided design (CAD) software for detailed design, and simulate and optimize the strength, stiffness and durability of the support roller through methods such as finite element analysis (FEA).
2: Material selection:
Select suitable cast steel or forged steel as the base material of the roller. These materials need to have good mechanical properties, such as high strength, high wear resistance and thermal fatigue resistance.
For special applications, alloy steel or other special materials may be selected.
3: Mold making:
Make sand molds or metal molds according to the design drawings. For large support roller, sand casting is usually used; for small-sized support roller with higher precision requirements, metal molds may be used for die casting or investment casting.
The mold needs to accurately reflect the shape and internal structure of the roller, including features such as mounting holes and bearing seats.
4: Melting and pouring:
The selected metal material is melted in an arc furnace, induction furnace or other type of furnace, and its chemical composition is adjusted to meet specific performance requirements.
After filtering and treating, the molten metal liquid is poured into the prepared mold for pouring. This process requires strict control of temperature and speed to ensure the quality of the casting.
5: Cooling and demoulding:
After pouring, the casting needs to be cooled naturally in the mold or quickly cooled by forced cooling.
After cooling to room temperature, the casting is removed from the mold. If it is sand casting, the sand particles remaining on the surface must also be cleaned.
6: Cleaning and preliminary inspection:
The casting is cleaned to remove excess burrs, fins and other impurities.
Preliminary quality inspections, such as appearance inspections and dimensional measurements, are carried out to ensure that the castings meet basic requirements.
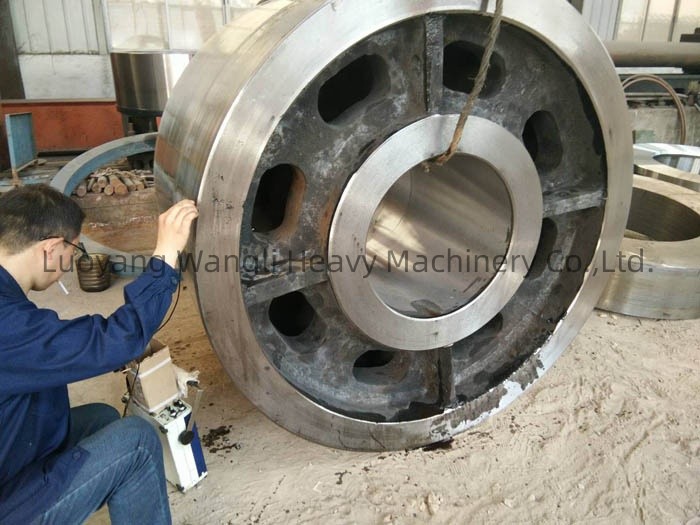

7: Heat treatment:
In order to improve the mechanical properties of the castings, such as hardness, toughness and ductility, the castings are usually subjected to heat treatment processes such as annealing, normalizing, quenching and tempering.
Heat treatment can eliminate internal stress and improve the wear resistance and service life of castings.
8: Machining:
Use lathes, milling machines, boring machines and other machine tools to finish the castings to achieve the required dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Machining includes but is not limited to: machining bearing seats, end faces, bolt holes and other parts.
9: Surface treatment:
In order to enhance the corrosion resistance of the support wheel and extend its service life, it can be surface treated, such as painting, galvanizing, carburizing, nitriding, etc.
10: Final inspection and testing:
After completing all processing steps, the support wheel is comprehensively inspected for quality, including dimensional accuracy, form and position tolerances, hardness testing, non-destructive testing (such as X-ray, ultrasonic flaw detection), etc.
If necessary, the support wheel should also be tested for dynamic balancing to ensure its stability under high-speed rotation.
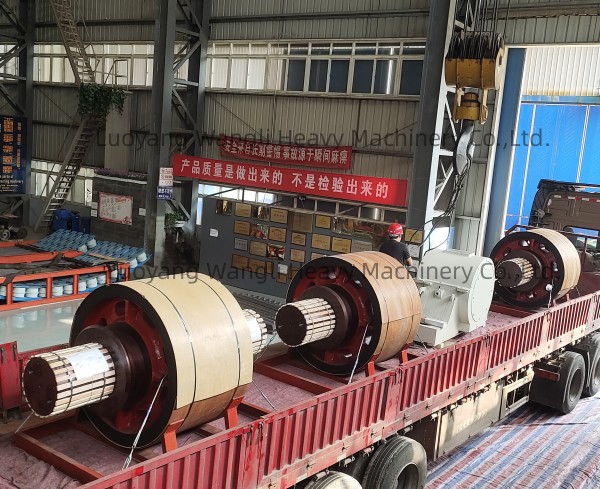
11: Packaging and delivery:
The support wheels that pass the final inspection will be properly packaged to prevent damage during transportation.
Arrange shipment according to customer orders to ensure timely delivery to users.

REQUEST A QUOTE
RELATED PRODUCTS

Customized cement kiln heavy duty 45# supporting roller

Customized Large Sliding Bearing Casting Seat

Customized Large dimeter rotary dryer 42CrMo forged ring
Welding ball mill spare parts Mill connection housing

Customized 35# casting Two segment spur girth gear copper mine mill


