Custom eccentric shaft with bearing seat
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Description

General processing flow of eccentric shaft with bearing seat:
1. Material selection and preparation
Material selection: Select suitable steel according to design requirements, usually high-strength alloy steel, such as 42CrMo, etc.
Cutting: Cut the selected raw materials according to the predetermined length.
2. Preliminary forging or casting
For some large or complex eccentric shafts, it may be necessary to form them by forging or casting.
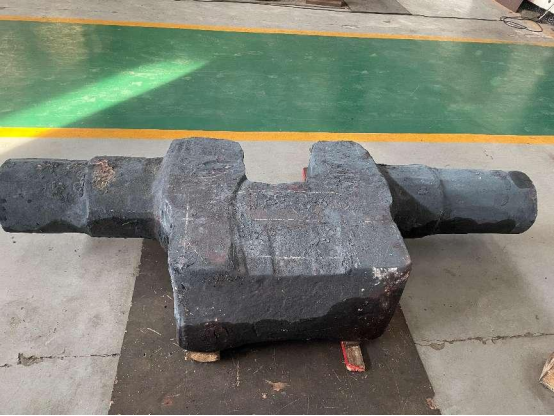

3. Rough turning
Rough machining: Preliminary turning of the eccentric shaft on a lathe to remove excess material and form a rough outline. The center hole is also drilled in this step.
Inspection: Check whether the dimensions after rough machining meet the process requirements.

4. Heat treatment
Quenching and tempering: In order to improve the hardness and wear resistance of the eccentric shaft, it is usually quenched and tempered. The specific heat treatment parameters depend on the material used.
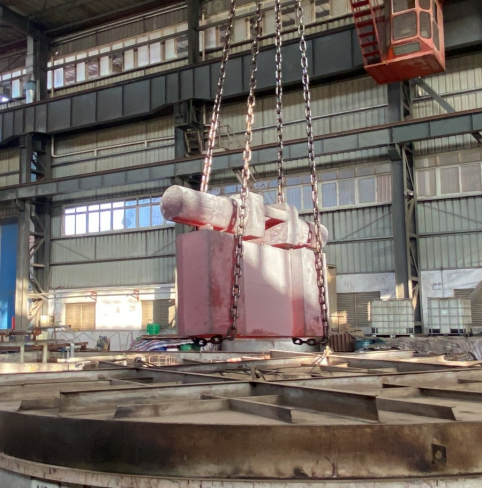

5. Semi-finishing turning
After heat treatment, semi-finishing turning is performed to further refine the dimensional accuracy of each part and prepare for subsequent processing.

6. Eccentric part processing
Eccentric positioning: Use special fixtures or chucks to properly fix the workpiece so as to accurately process the eccentric part.
Precision grinding: For the key surfaces of the eccentric shaft, especially the eccentric part, high-precision grinders are used for fine grinding to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
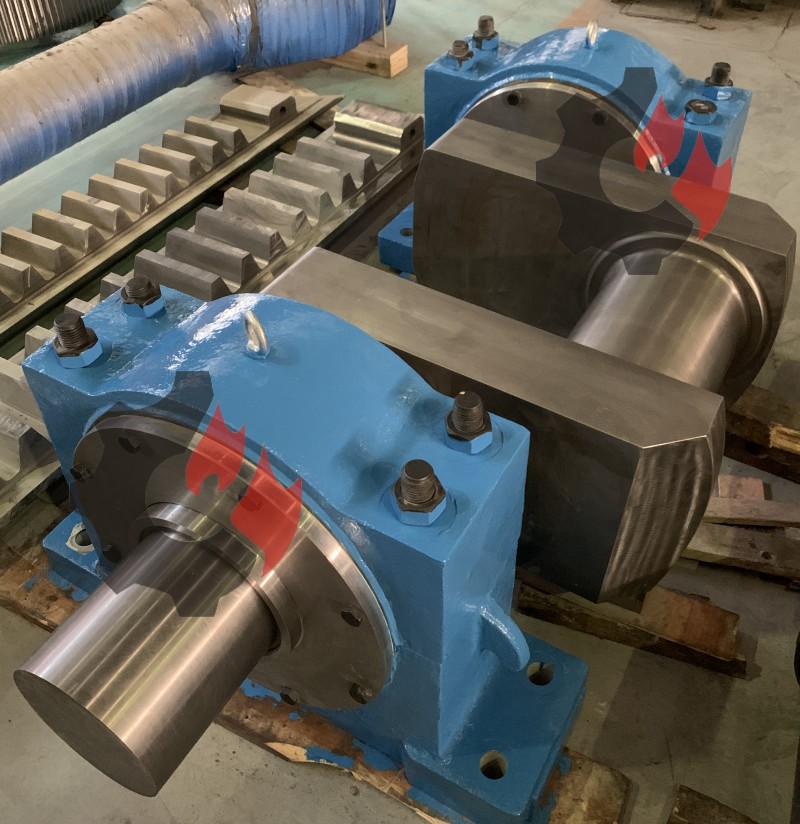
7. Bearing seat processing
Eccentric shafts with bearing seats require special attention to the processing quality of these parts. Including but not limited to:
Boring: Use a boring machine to perform precision boring on the bearing seat hole to ensure that the hole diameter tolerance, roundness and surface roughness meet the requirements.
End face processing: Ensure the perpendicularity between the end face of the bearing seat and the axis.
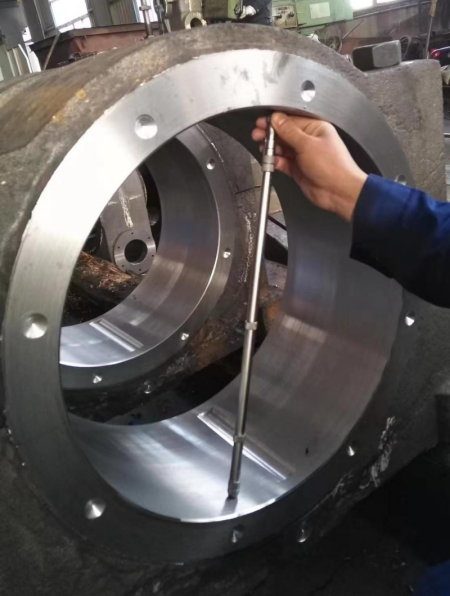

8. Final finishing
Depending on the specific design requirements, additional finishing steps may be required, such as keyway milling, thread processing, etc.

9. Surface treatment
It may involve surface hardening treatments such as chrome plating and nitriding to enhance corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
10. Inspection and testing
Dimension inspection: Use tools such as three-coordinate measuring machines for comprehensive dimensional inspection.
Nondestructive testing: such as magnetic particle testing, ultrasonic testing, etc., to check whether there are cracks or other defects inside.
Dynamic balancing test: Especially for eccentric shafts running at high speed, dynamic balancing correction must be performed.
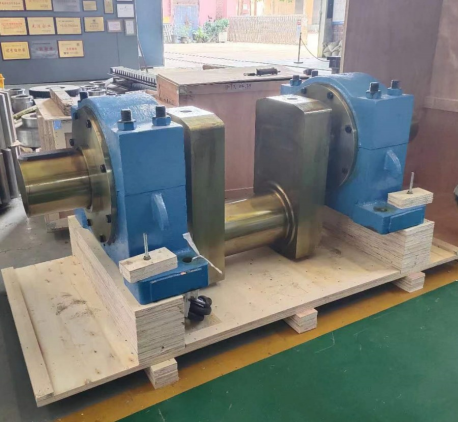

Application scenarios of eccentric shafts: What mining equipment are they mainly used on
1. Vibrating screen: The eccentric shaft is used to drive the vibrator of the vibrating screen. The centrifugal force generated by the rotation makes the screen vibrate, which helps the screening and grading of materials.
2. Crusher:
Jaw crusher: The eccentric shaft is one of the core components of the jaw crusher. It is connected to the movable jaw plate. When the eccentric shaft rotates, it drives the movable jaw plate to swing periodically, thereby achieving the extrusion and crushing of the ore.
Cone crusher: Although it mainly relies on the relative movement between the inner and outer cones, eccentric shafts are also used in some designs to provide the necessary motion trajectory.
3. Vibrating feeder: Driven by the eccentric shaft, the feeder can vibrate at a certain frequency and amplitude to ensure that the material is evenly supplied to the subsequent processing equipment.
4. Sand washing machine: In some types of sand washing machines, the eccentric shaft is used to drive the drum or screen to produce vibration operation, helping to clean and separate the dirt and other impurities in the sand.
5. Conveyor (specific type): Some specially designed vibrating conveyors use the vibration generated by the eccentric shaft to push the material forward, which is particularly suitable for transporting fine particles or viscous materials.
6. Dewatering screen: Similar to the vibrating screen, the role of the eccentric shaft here is also to generate enough vibration to effectively remove the moisture from the mineral.
7. Other auxiliary equipment: Some types of agitators, cooling towers, etc. may also use eccentric shafts to produce the required movement pattern.
REQUEST A QUOTE
RELATED PRODUCTS

Spur gear shaft forging high quality large diameter for Ball Mill

Mining Machinery parts Casting Jaw Crusher Jaw Plates

Custom forged 42CrMo large modulus gear shaft

Rotor Shaft for Crusher

Custom Forging Large Roller Shell High Quality Briquetting Machine Roll Shell Dimpled Roller Shell