Mining custom forging large module helical gear shaft
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Description
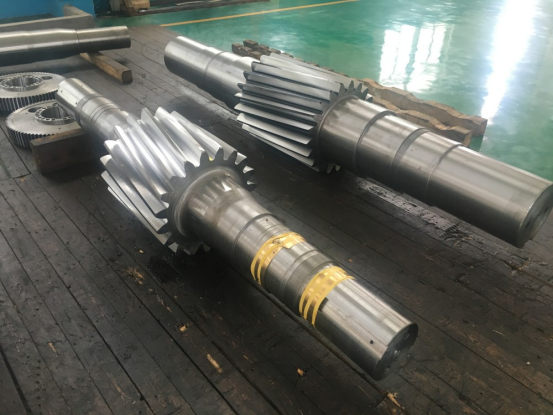

Helical gear shaft production process
1.Forging
Large modulus heavy helical gear shafts usually use high-strength alloy steel (such as 42CrMo, 35CrMo, 20CrMnTiH, etc.) to meet high load and wear resistance requirements. Ensure that the raw materials are free of inclusions, pores or cracks to avoid defects during the forging process. Use large forging equipment (such as 10,000-ton hydraulic presses or hammer forging machines) to provide sufficient pressure to form large modulus gear shafts. Ensure that the equipment can withstand the weight of the parts and the impact force required for forging. The forging ratio of large modulus heavy helical gear shafts is usually 2~4, and the specific value needs to be adjusted according to the material properties and part shape. A forging ratio that is too small may cause uneven internal structure of the material, while a too large ratio will increase energy consumption and cost.

2. Rough machining
Dimensional accuracy: The dimensions of each part should be close to the design value, but sufficient machining allowance must be left.
Shape accuracy: Key parts such as journals and gear tooth shapes must meet basic shape requirements.
Surface roughness: The surface roughness after rough machining is usually Ra6.3~Ra12.5.
Coaxiality and verticality: ensure that the positional relationship between each part meets the design requirements.

3.UT
UT after rough machining is an important step to ensure the internal quality of parts, especially in the manufacturing process of key parts such as helical gear shafts. Ultrasonic testing can detect internal defects (such as cracks, pores, inclusions, etc.) that may exist after rough machining, so as to avoid these problems affecting the quality of subsequent heat treatment and finishing.
4.Quenching and tempering
Improve the overall mechanical properties of parts, including strength, toughness and hardness, and provide a good material basis for subsequent finishing and use. Improve hardness and strength through quenching, and eliminate the internal stress generated by quenching through high-temperature tempering to increase toughness. Create good conditions for subsequent finishing and reduce tool wear and processing difficulty.
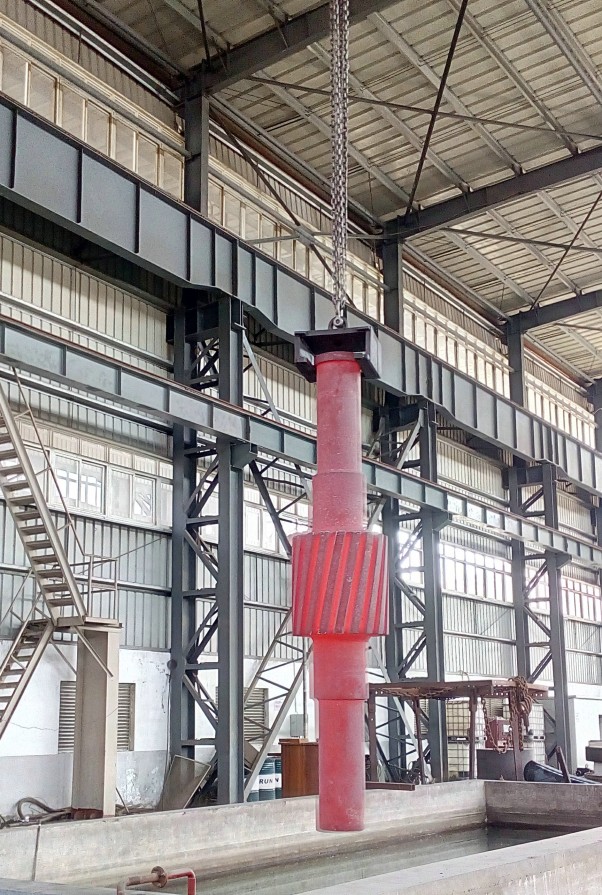

5. Finishing
By removing the excess left after quenching and tempering, the parts can meet the dimensional tolerances required by the design drawings. Improve the surface roughness of parts and reduce friction and wear. Ensure that the shape and position accuracy of parts such as journals, gear teeth, keyways, etc. meet the use requirements. During finishing, pay attention to the high hardness of the material after quenching and tempering, and adjust the cutting parameters to avoid excessive wear of the tool. There may be residual stress in the parts after quenching and tempering, and measures should be taken to prevent deformation during processing.
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness not up to standard | Improper cutting parameters or tool wear | Adjust cutting parameters, replace tools |
| Dimensional tolerance exceeded | Inaccurate positioning or machine error | Calibrate machine, improve positioning accuracy |
| Gear tooth profile error | Incorrect settings on hobbing or shaving machine | Calibrate machine parameters, check tool condition |
| Workpiece deformation | Release of residual stress or improper clamping force | Optimize machining sequence, reduce residual stress |
6. Finished product inspection
After finishing, we will conduct finished product inspection on the helical gear shaft to ensure that the helical gear shaft meets the design requirements and performance. In addition to dimensional inspection, we will also conduct ultrasonic testing to check whether there are cracks, pores or other defects inside the parts. Magnetic particle testing is used to detect cracks or defects on the surface and near the surface.

7. Packaging
We will perform rust prevention and packaging according to customer requirements.

REQUEST A QUOTE
RELATED PRODUCTS

Custom forged steel large helical gear shaft

Customized hammer crusher long service life wear resistant rotor shaft

34CrNiMo6 Alloy steel Helical gear shaft rotary kiln

Nonstandard custom forging steel large flange shaft

Customized AISI4140 heavy duty hammer crusher Rotor Shaft