How do you properly mount gear on a shaft?
Mounting a gear onto a shaft demands a thorough analysis of the application’s specifications, including torque, load, alignment, maintenance requirements, etc. Here is a structured way to ensure a strong and efficient installation:
Understand Application Needs: Begin by clearly defining the operational conditions for the gear and shaft, such as the level of torque transmitted, types of loads encountered (radial, axial, or a combination thereof), operational speeds, and environmental factors.
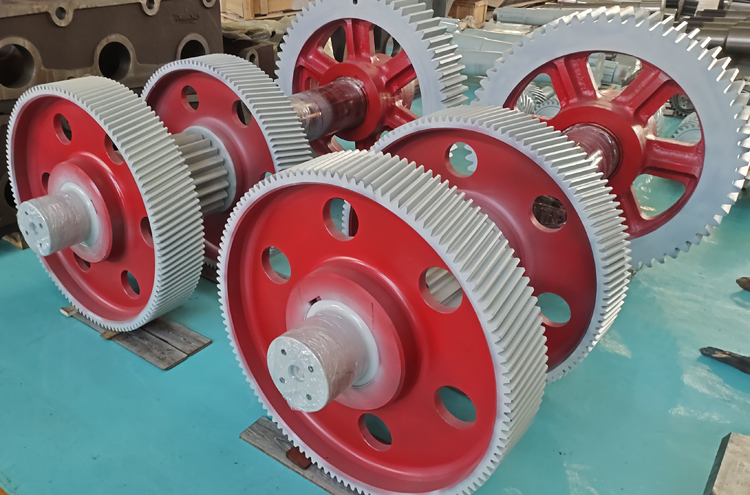

Gear shaft
1. Evaluate Application Needs: Begin by clearly defining the operational conditions for the gear and shaft, including the magnitude of torque transmitted, types of loads encountered (radial, axial, or a combination thereof), operational speeds, and environmental factors.
2. Select Appropriate Mounting Methods: Based on the application’s condition, choose the most suitable method for assembling the gear to the shaft. Standard methods include keyway fits, setscrew locking, shrink fitting, and spline connections. Each method has its characteristics and is applicable to different application scenarios.
– Set Screws: Simple and cost-effective. Ideal for low-torque applications. Ensure the shaft has a flat spot for the screw to grip.
-Key and Keyway: This is common for medium to high torque. Use standardized keys (e.g., square, Woodruff) and machine-match keyways on the shaft and gear.

keyways pinion shaft
-Press Fit: This provides a tight interference fit. It is suitable for high-torque but requires precise machining. Use thermal expansion (heat gear/superb shaft) for assembly.
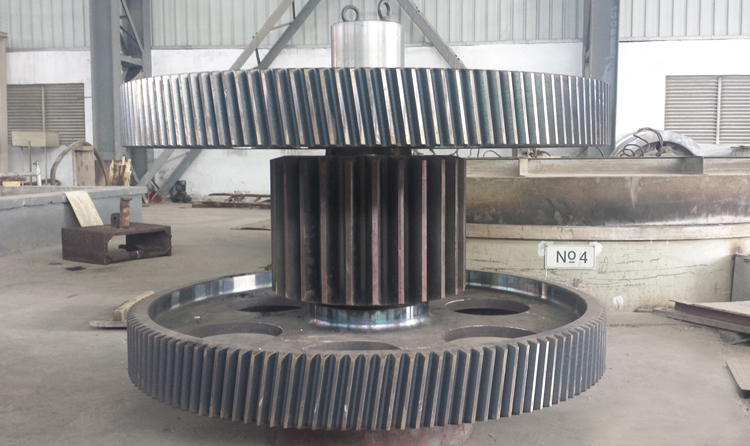

Gear shaft assemble
-Splined Shafts are for high torque and adjustable positioning. They are more complex and costly but offer flexibility.
-Tapered Bushes/Lock Collars: These allow easy adjustment and disassembly. Tighten a nut to compress the bushing onto the shaft.
– Flanged Mount: Bolt the gear to a flange on the shaft. Common in heavy machinery.
– Retaining Rings/Circlips: Prevent axial movement; pair with other methods for rotational security.
3. Preparation
– Clean Components: Remove debris from the shaft and gear bore.
– Machine Surfaces: Create keyways, splines, or flat spots as needed. Ensure bore and shaft dimensions match (interference fit for press fit).
-Check Tolerances: Verify fit (sliding, transition, interference) based on the method selected.
4. Alignment
– Axial Alignment: Position the gear at the correct location on the shaft.
– Radial Alignment: Use alignment tools (dial indicator) to ensure the gear is perpendicular to the shaft axis.
5. Fixed the Gear
– Mechanical Fasteners: Tighten set screw or lock collars to the required torque. For keyway gears, insert the key and push the gear into position.
– Press Assemble: Apply lubricant and use the hydraulic press for installation.
Thermal Methods: Heat the gear or cooling the shaft.
6. Testing and Validation
Visual Inspection: Check the installation of the gear and shaft to ensure they are not damaged and are correctly aligned.
Operational Check: Check axial and radial runout, paying attention to any unusual noises or vibrations.
Functional Test: Rotate the shaft to confirm the gear operates smoothly. If possible, conduct the test under load conditions.
7. Common Errors and Prevention
Improper fit: Ensure the gear bore matches the shaft diameter very well as the standard.
Misalignment: Avoid misalignment that can lead to wear and vibration.
Over-tightening: Prevent damage to threads or components by avoiding excessive tightening.
Environmental Factors: Consider the effects of thermal expansion and corrosion, choosing appropriate materials and protective measures.
If you need gear/pinion shaft, don’t hesitate to get in touch with luoyang wangli heavy machinery co.,ltd: lulu@citicwl.com