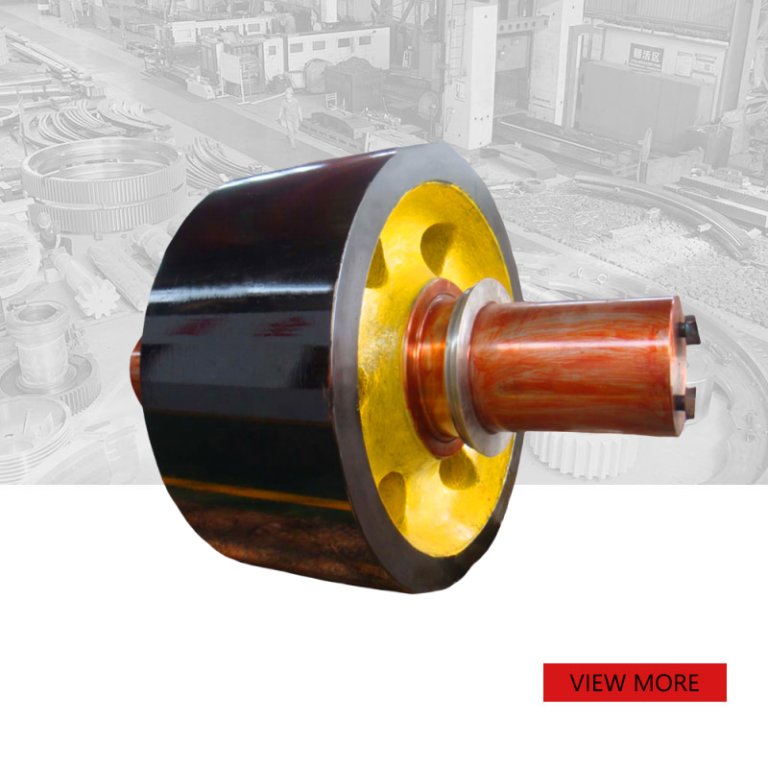
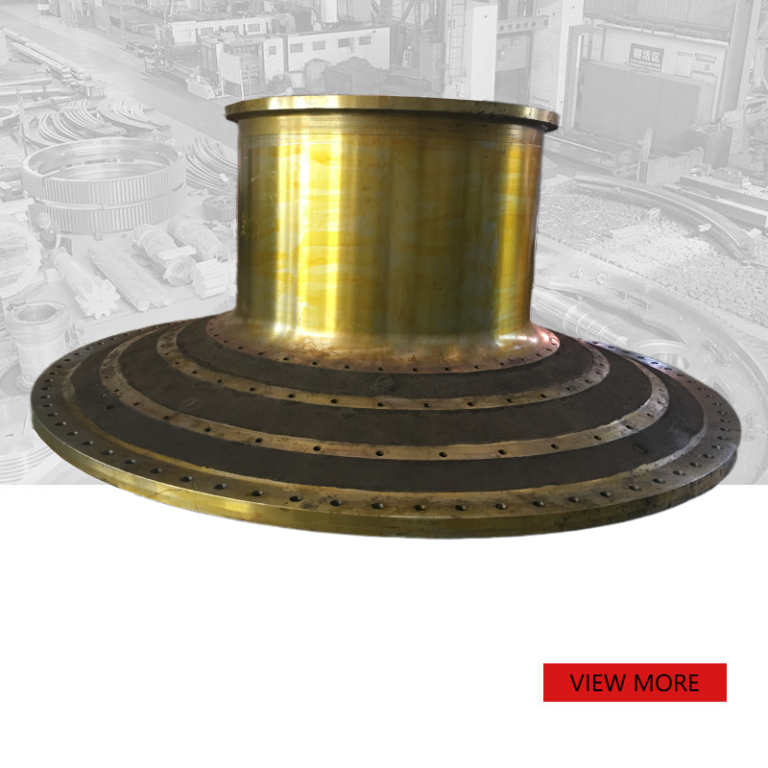
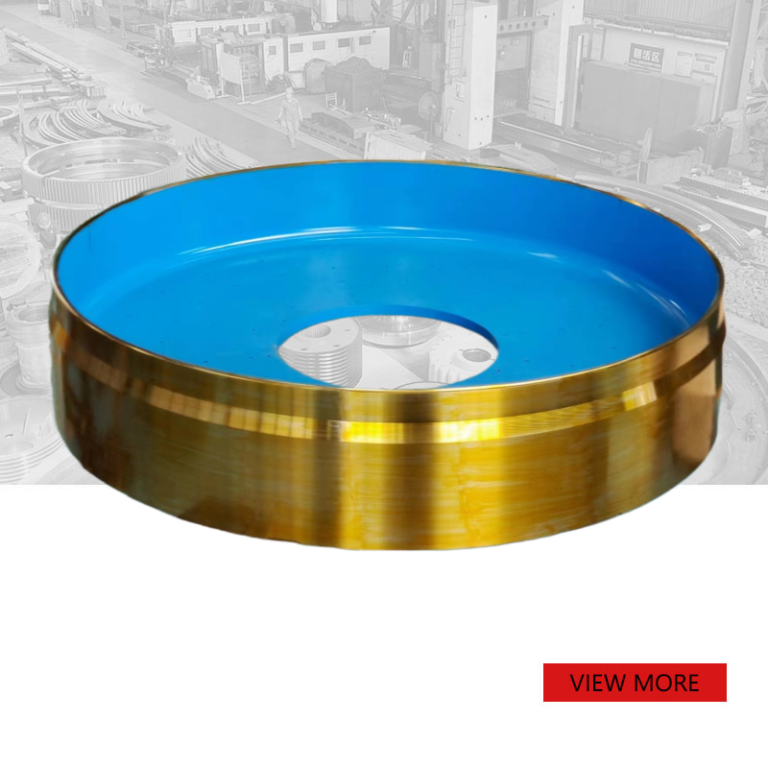
Custom forging large support roller
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Description
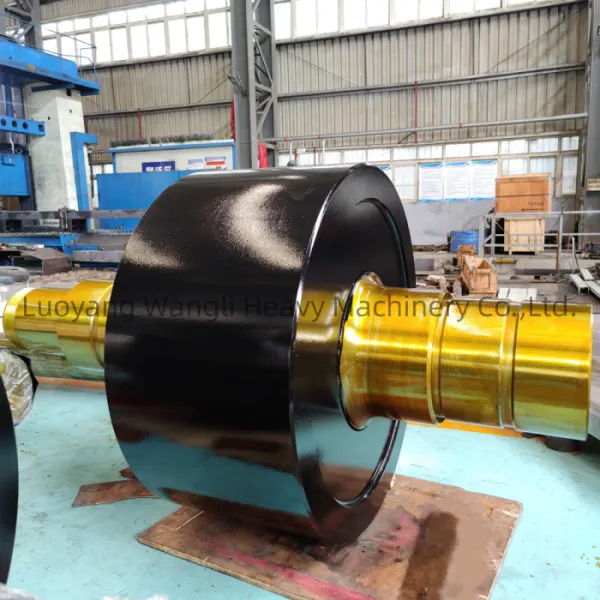

We produce support roller according to customers’ drawings and requirements.
The general processing flow of forged support wheels:
1: Design and engineering analysis:
First, it is necessary to carry out a detailed design according to the specific needs of the rotary kiln and optimize the structure and performance of the support wheel through tools such as computer-aided design (CAD) and finite element analysis (FEA).
Determine the size, shape, tolerance and other technical requirements of the forging.
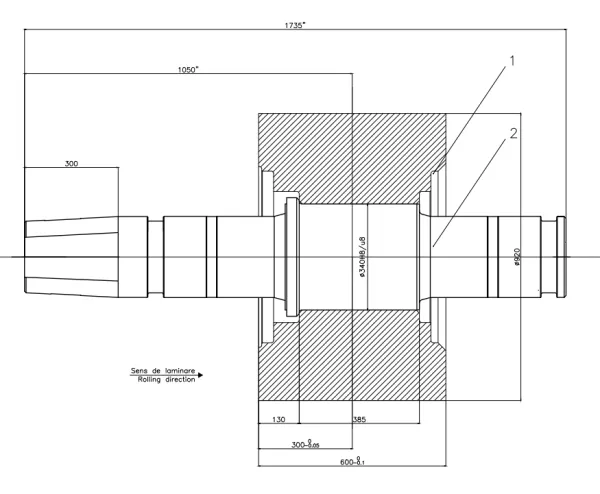
2: Material selection:
Select steel or alloy steel suitable for forging, such as high-quality carbon steel, alloy structural steel, etc., which have good forgeability and mechanical properties.
According to the specific application scenario, it is necessary to consider heat resistance and wear resistance factors to select materials.
3: Billet preparation:
According to the size and weight of the required support wheel, cut out the appropriate size of metal billet (usually cylindrical or square).
The chemical composition and physical properties of the billet meet the design requirements and are strictly inspected.
4: Heating:
Put the billet into a resistance furnace, gas furnace or induction heating equipment for preheating to a suitable forging temperature (generally between 800°C and 1250°C, depending on the material type).
During the heating process, the heating should be uniform to avoid excessive temperature gradients that may cause the blank to deform or crack.
5: Forging:
Use a forging press, hydraulic press or hammering equipment to apply pressure to the heated blank to form it according to the shape of the die.
Forging can be divided into free forging (without using a die), die forging (using a fixed die) and ring forging (for making ring parts).
For large support rollers, a multi-step forging process may be used to approach the final shape gradually.

6: Cooling and heat treatment:
After forging, the support roller needs to be cooled naturally in the air or quickly cooled by water cooling, oil cooling, etc.
After cooling, the support roller is usually heat treated, such as normalizing, quenching, tempering, etc., to adjust its mechanical properties, eliminate internal stress, and improve hardness and toughness.
7: Rough machining:
The initially formed support roller is roughly machined to remove excess material and form a rough outline.
This step includes turning the outer circle, end surface machining, drilling, etc., to prepare for subsequent finishing.

8: Finishing:
Use high-precision machine tools to finish the key parts of the support wheel to ensure that the dimensional accuracy and surface finish meet the design requirements. The processing content mainly includes the fine processing of important positions such as bearing positions, mounting holes, raceways, etc.
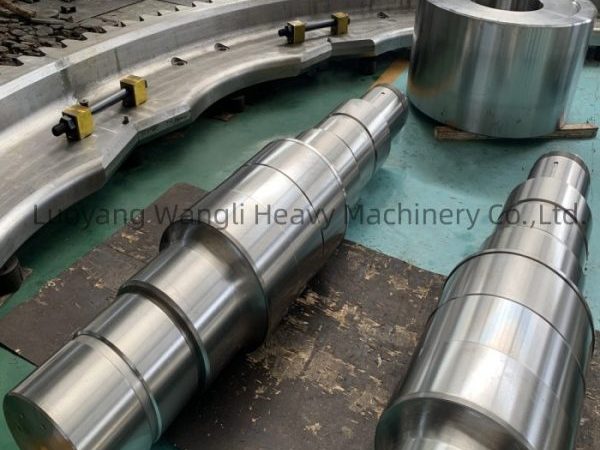

9: Surface treatment:
In order to enhance the corrosion resistance and extend the service life of the support wheel, surface treatment such as painting, galvanizing, carburizing, nitriding, etc. can be carried out. Surface treatment can also improve the wear resistance and friction characteristics of the support wheel.
10: Quality inspection:
After completing all processing steps, the support wheel is comprehensively inspected for quality, including dimensional accuracy, form and position tolerance, hardness test, non-destructive testing (such as X-ray, ultrasonic flaw detection), etc. If necessary, the support wheel can be dynamically balanced to ensure stability under high-speed rotation.
11: Packaging and delivery:
The support wheel that passes the final inspection will be customized according to the needs to prevent damage during transportation. Arrange delivery according to the customer’s order to ensure timely delivery to the user.