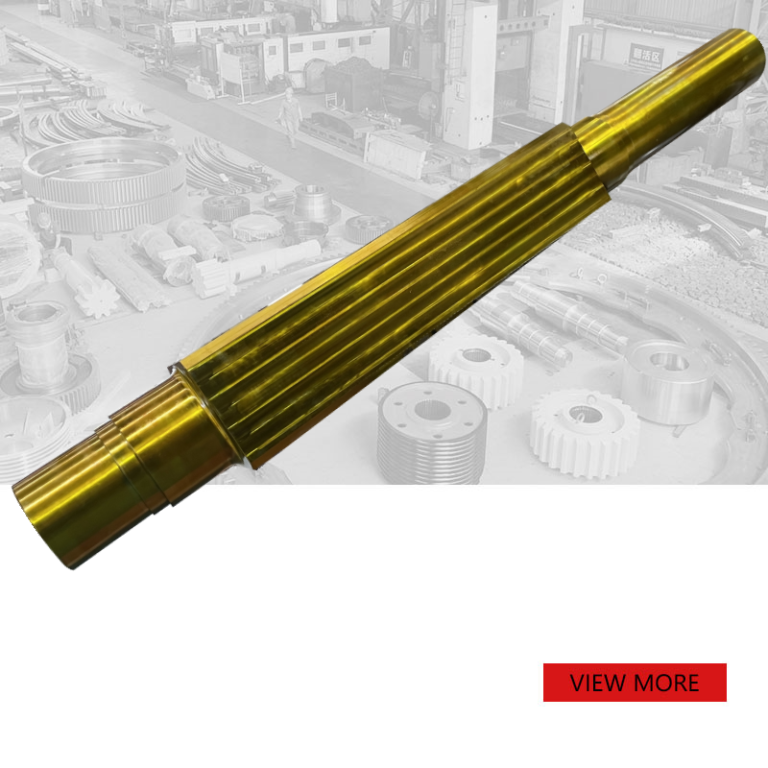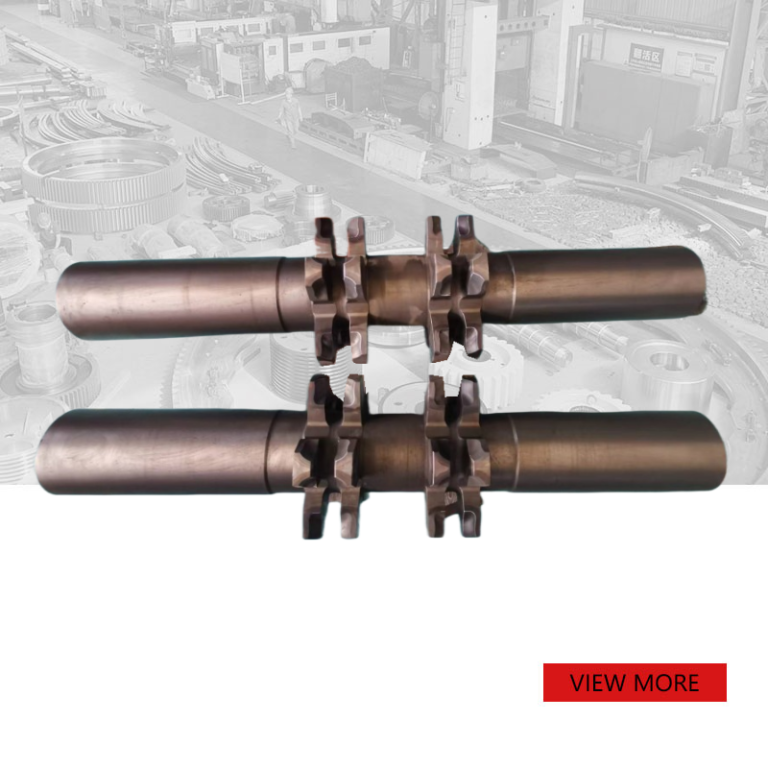
Rotor Shaft for Crusher
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Description
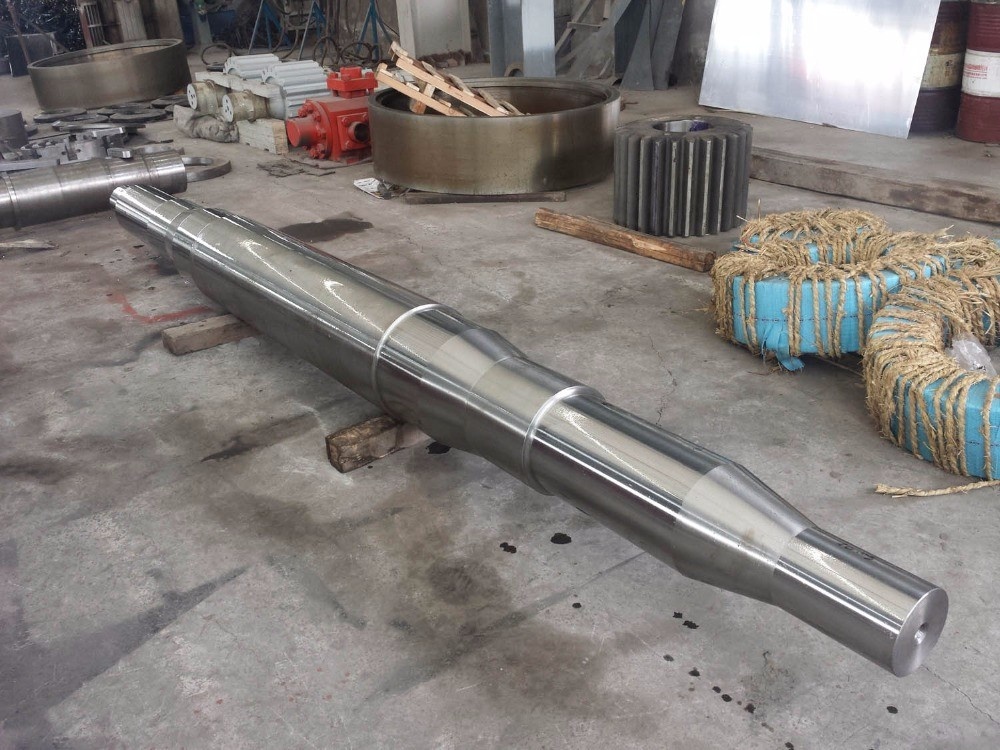

Overview of Rotor Shaft
Rotor shafts are critical components in various types of machinery, particularly in rotating equipment such as turbines, motors, pumps, and compressors. The rotor shaft is the central part around which other components are assembled and is responsible for transferring mechanical power from a source (like an engine or motor) to a load (such as a generator, propeller, or wheel).
Production process of Rotor Shaft
Material Selection:
Common materials include carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and in some cases, titanium or other specialized alloys.
Forging or Casting:
Forging: The selected metal is heated and shaped by hammering, pressing, or rolling into the general shape of the shaft. This process can improve the grain structure and mechanical properties of the material.
Casting: Molten metal is poured into a mold that has the shape of the shaft. This method is more suitable for complex shapes but may not provide the same mechanical properties as forging.
Machining:
Rough machining: Initial shaping using lathes, milling machines, or CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines to remove excess material and form the basic shape.
Precision machining: Fine-tuning the dimensions and surface finish to meet tight tolerances, which might involve turning, grinding, drilling, and tapping operations.
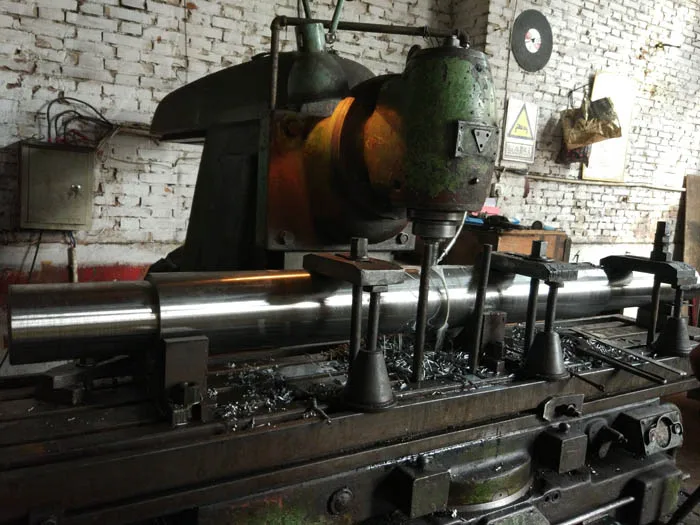

Heat Treatment:
Hardening: Heating the shaft to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooling it to increase hardness and strength.
Tempering: Reheating the hardened shaft to a lower temperature to reduce brittleness and adjust the hardness to the desired level.
Other treatments like carburizing, nitriding, or induction hardening may be applied depending on the application requirements.
Surface Treatments:
Processes such as plating, coating, or polishing may be used to protect against corrosion, improve wear resistance, or achieve a smooth finish.
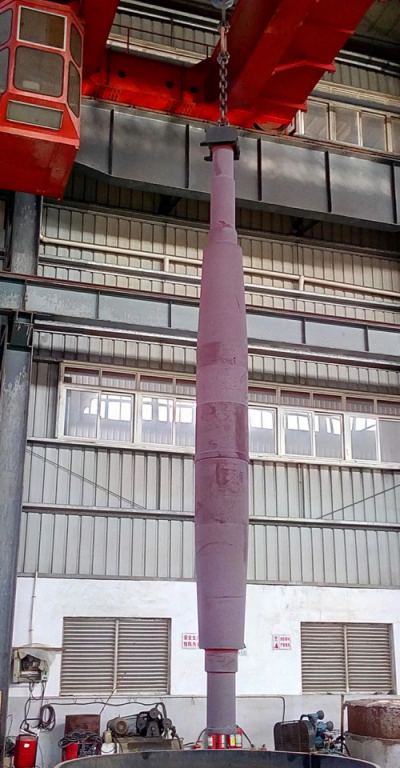

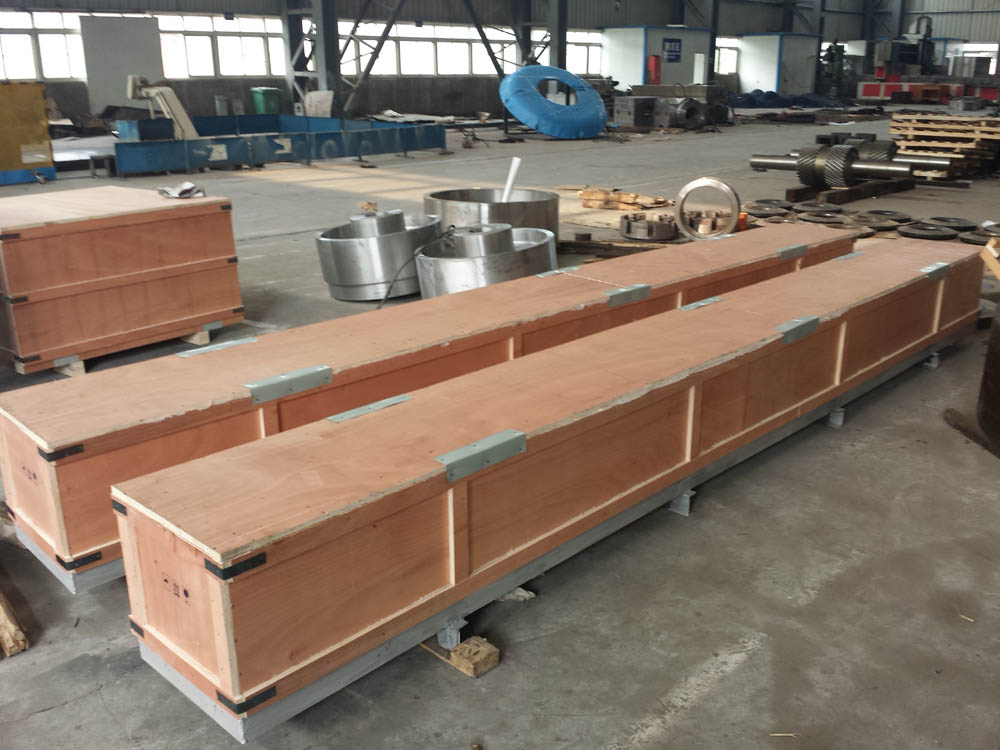
Package of Rotor Shaft
Oiling or Coating: Applying a thin layer of rust-preventative oil or another protective coating can shield the surface from moisture and contaminants.
Packing: fumigation-free wooden case customized according to product size. If necessary, a steel frame will be welded to the outside of the wooden box to assist the operation of the forklift truck.

Application of Rotor Shaft
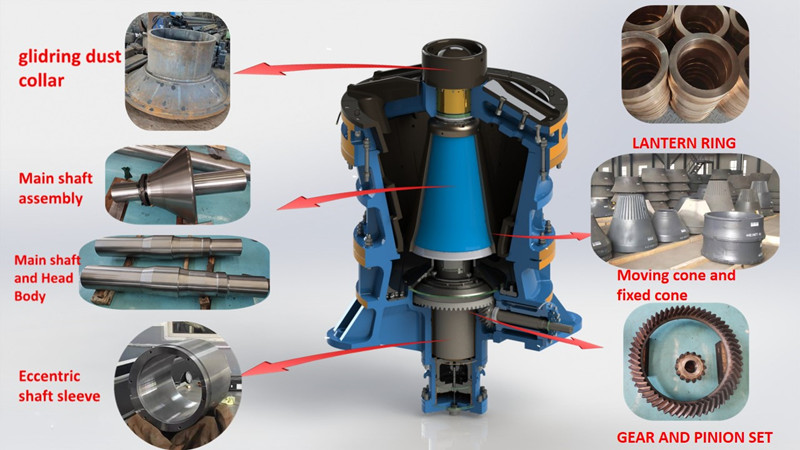
This type of rotor shaft is mainly used in impact crushers and sends you in time crushers. We also produce spindles for jaw crushers and cone crushers.
The rotor shaft is also used in the mill:
Ball mill: The rotor shaft (cylinder shaft) supports the entire cylinder and rotates it through the transmission system, and the steel ball or gravel inside grinds the ore during the rotation.
Autogenous and semi-autogenous mills: These devices rely on the ore itself and a small amount of added grinding media, rolling friction in the cylinder to achieve grinding purposes, also rely on a strong rotor shaft to transfer power.
FAQs of Rotor Shaft
— How do I know if my machine needs a new rotor shaft?
–If you observe abnormal vibration, noise, increased temperature, or decreased performance, it may be a sign of a problem with the rotor shaft. Regular preventive maintenance checks and monitoring the status of the rotor shaft with tools such as vibration analysis can help identify problems in advance. Once significant wear, cracks or other structural damage is found, replacement should be considered.
–Can the rotor shaft be repaired or must it be replaced?
–Minor surface damage, such as scratches or shallow corrosion, can be repaired by sanding, welding or coating. However, for more serious damage, such as cracks, bending or deep corrosion, it is recommended to replace the entire rotor shaft to ensure safety and reliability.
–How does the material choice of the rotor shaft affect me?
–Different application scenarios have different requirements for the material of the rotor shaft. For example, when working in high temperature environment, you can choose heat-resistant steel; In corrosive environments, stainless steel or nickel-based alloys should be considered. The right materials not only increase durability, but also reduce maintenance costs.







